Shifting the Muscle to Fat Ratio: Women-Specific Body Composition Considerations

In this article (clickable table of contents):
- I. The research has been skewed and gender biased for too long
- II. Common issues I hear women struggle with – do any of these apply to you?
- III. Understanding that body composition is NOT “your weight on the scale”
- IV. Creating an optimal state in the body to drive the results you want
- V. Building muscle and losing fat at different stages of your menstrual cycle
- VI. Building muscle and losing fat for women in peri and post menopause
- VII. For women of all ages: why we need to eat balanced meals with whole foods
- VIII. The importance of fueling (not fasting) around your workouts and how to do it
- IX. Why reduced stress and quality sleep are also essential for body composition shifts
- X. Wrap up and recommendations for additional learning
I. The research has been skewed and gender biased for too long
Many women I talk to are still subscribing to outdated myths about training and are stuck in an “exercise more, eat less” mentality that is robbing them of the strong, healthy body they deserve from the effort and time they put into their training.
I want to clarify from the start of this article that I’m aware of and respect that people have different goals for their physique and different lifestyle practices they are comfortable with, and that what I am focused on in this post is helping you better understand how your body works so you can become physically stronger, more capable and confident, and enjoy a high quality life in a functional body at every age.

It’s time to bust some myths and give you the information you need to support your body’s process of getting stronger and healthier so you can stop undermining all the effort you put in with diet culture myths or strategies that come from research done on men, not women.
The changes we go through in life in our incredible female bodies – from puberty to menopause and everything in between – deserves attention and understanding. We are often on our own figuring everything out with so much scientific research in the past being done on men only, and the perception of a woman’s cycle as “too complex” (1).

This gender biased research means many (fortunately not all) doctors and other professionals fail to address women’s hormone concerns adequately, dismiss their concerns entirely by suggesting “it’s just part of the aging process” or “it’s in your head” or suggest strategies that fail to address the root cause of the issues.
When researching this post for example, I found the lack of female representation in research studies appalling. It is only in recent years that women have been included more frequently, and yet even in many of the studies that included women there was rarely any differentiation in phases of the menstrual cycle, or attention to women at different stages of life. And even less that examined women of different cultures and ethnicities to explain how women from different backgrounds might experience things like peri menopause, strength gains and fueling needs.
As a result, generalizations are made because of the design of the research studies. No wonder it has been challenging for us to get good, relevant information that works for us! I will present to you what I have learned from what is currently available, but I too am still looking for more. See recommendations for follow up at the end of this article.
II. Common issues I hear women struggling with – do any of these apply to you?
- “I eat healthy but I’m not losing weight.” Over focusing on “weight loss” without understanding body composition can skew your perception of results.
- “I am super low carb, but I keep having sugar cravings.“ Low carb diets create eating imbalances and metabolic disruption in active women.
- “I’m afraid to take rest days, but I am starting to feel less motivation.” Overtraining leads to low energy and heightened inflammation.
- “I do an extra hour of cardio after my other workout but I still am not getting leaner.” Overtraining and excess cardio can increase inflammation, elevate cortisol, lead to muscle breakdown, and impact metabolic health.
- “I do fasted training every day, but I’m still not seeing results.” Women do better in a fed state than a fasted state with their workouts.
- “I just went through menopause and I’ve gained 15-20 pounds.” Lack of understanding of how to adjust training and nutrition strategies in this life stage leads to increased fat gain and loss of muscle.
III. Understanding that body composition is NOT “your weight on the scale”
Due to over-focus on “weight loss” many women are more focused on seeing a scale number go down rather than on how they can lose body fat and increase lean mass (2)(3).
If we take a closer look at body composition, we can shift this mentality and start to understand why even when we sometimes lose “weight” doing fad diets it comes right back, and that we’re sacrificing our valuable muscle tissue in an effort to lose this “weight”(4).
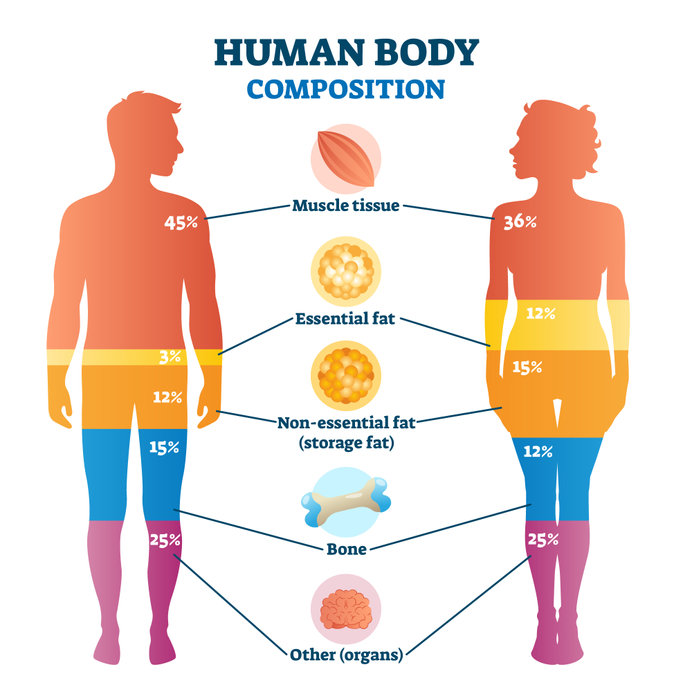
Weight on the scale measures overall body weight, which includes muscle, bone, water at the time of weighing, body fat and all the body tissues combined. Because many of these factors are variable (have you eaten, how much water are you retaining, what time of the month is it, have you had a bowel movement today), it’s more ideal to measure the composition of fat and muscle tissue on the body rather than body weight alone, which does not take the ratio of these important tissues into consideration.

Two women, one with more muscle and less fat and one with more fat and less muscle might weigh the exact same number on the scale. But the woman with more muscle will look leaner and more compact, and the woman with more body fat will look thicker.
While a pound of muscle and a pound of fat both weigh one pound, the pound of fat takes up more space than the pound of muscle, due to its structural composition.
This is why taking a closer look at the ratio of muscle to fat on your body matters far more than the “amount you weigh.”
To get a real body composition measurement, ideally you would use a professional method like the DXA scan (dual x ray absorptiometry), air displacement plethysmography (i.e “Bod pod“), bioelectrical impedance measurement (i.e. InBody scan or similar), 3-D body scanner, or other professional body composition measuring test.
However as these are not always readily available, other methods may be useful for self testing, including skin caliper measurements, measurements with a tape measure around the hips, thighs, arms, stomach and chest, and full length photos from the front, side and back wearing the same or similar garments.
While it’s absolutely fine to weigh yourself in addition to these methods when looking for changes, only weighing yourself will give you very little data that speaks to your body composition. Combined with an over focus on “weight loss” along with the cultural expectations of women and their bodies, many women have disordered eating (5), disordered self perception, and are following fad diets, skipping meals, under-eating and overtraining.

They end up constantly down on themselves for their perceived lack of progress, under nourished, stressed-out and set themselves up for unintended health consequences including an increased risk for bone stress injury and cardiovascular disease (6).
This heightened stress state from overtraining and under fueling (not to mention stressing about our weight and every other pressure we feel from societal expectations) elevates our cortisol and increases the inflammatory response, which not only breaks down muscle but also creates fat storage and has a detrimental impact on our mood, energy levels, and long-term metabolic rate and overall health (7).
While some “weight loss” may be observed, this often comes back quickly, and the manner in which the weight is lost has unintended consequences that do little to contribute to a highly functional, strong body. All this focus on our weight and the vicious cycle we get in when we constantly seek shortcuts to lose it can undermine our long-term health and a good quality of life, increase negative self talk, and contribute to the perception that our appearance is the main driver of our value and worth.
While fat loss is a goal that a lot of women have and equate to “weight loss,” not enough women have the goal of gaining or preserving muscle, and as a result they are losing out – especially during the important transition from regular menstruating years to peri and post menopause – a time when the body’s fluctuating estrogen and progesterone signals become irregular and eventually stop, impacting our ability to lose fat and build muscle the same way.
The reason I say we as women are losing out is because muscle is metabolic currency (8). When we focus on strengthening, growing and preserving our muscle tissue, we start training, eating and resting in smarter ways, ways that go beyond aesthetics and support our long-term health – and as an added bonus, frequently have an aesthetic result as a natural byproduct.
I discussed this in depth, along with the ramifications this has on women in a recent podcast with Dr. Stacy Sims, and Rock Your Life member Amanda had this to say about how it impacted her:
Understanding body composition and setting goals with that as a primary focus rather than on weight loss is truly a mindset game changer.
As Amanda points out, this unhealthy focus on having someone else’s idea of a “perfect body” is one of the root causes of the problem that creates so much stress and pressure on women. I want to thank the Rock Your Life members for all the discussions we have had (and continue to have) about these topics, as they have been a tremendous inspiring for me in writing this article and clarifying points that I wanted to make.
IV. Creating an optimal state in the body to drive the results you want
In order to see a body composition change, we need to create an optimal state in the body for our hormones to do their work to support muscle growth and support fat loss. It is not “calories in/calories out” or how many workouts you do vs. how little you eat.
If you are over focused on your workouts as the sole driver of seeing results or losing weight like a lot of women are, it’s easy to get into a “no days off” training mindset. But consider that your workouts are like seeds you are planting, and like any seed you want to see grow and flourish they need to be planted in fertile soil, and have sunlight and rain to grow and thrive.
Your nutrition focus is the fertile soil, and your sleep and stress management are your sunshine and rain. Your workouts will not “take root” and grow a strong body without these other essential components repeated consistently. Too much rain can wash a seed out of the soil, like too much stress can sabotage your results.

I’ll talk more about calories shortly, but suffice to say that you cannot see your body flourish and grow strong if you are constantly restricting your nutrient intake and not paying attention to the quality of the nutrients you eat. Poor quality soil impacts the growth of a plant, just like lack of quality nutrients will impact the efficacy of your workout. A plant grows in the presence of all of these nurturing variables in balance, and it takes a little time.
Your results will never happen without the combination of these actions (Sleep, Nutrition, Stress Management, Exercise) repeated, and you being patient and allowing the results to unfold.
Plants grow faster when they’re given all these resources, and your body will respond when you give it what it needs to thrive as well. That’s why we have what I refer to as the “4 Pillars of Health,” these 4 aspects of your life that only you can control and that work together to create that optimal state in your body.

With more of a focus on eating, sleeping, stress reduction and training to support your energy and valuable muscle tissue, you’ll have an easier time regulating your body composition at every stage of life, and you’ll feel stronger and healthier in the process. You will be less susceptible to advertising for “weight loss products” that prey on culturally created fears of women being undesirable (what a load of garbage).
Having a focus on growing and preserving our muscle, especially as we age is a great idea. Not only does muscle surround and protect our joints and organs, it secretes protective cytokines which boost your immune response during contraction (9) (10).
On the aesthetic front (how we look), muscle is dense and compact so as you add it to your frame you will become physically smaller and have a more toned appearance as discussed above. We burn more fat more easily when we’re more muscular (11), and that valuable muscle tissue has other protective benefits to our bodies as well. You’ll be physically stronger, enjoy a more robust immune response (9), and boost your sense of capability and confidence.
Focusing on muscle, and training strategies to grow it will not necessarily “bulk you up.” Getting muscularly large for women is achieved through years of intentionally working towards that goal, with targeted training and a lot of fuel. “Bulky” may mean different things to different people, but I feel that the fitness industry has created a fear of things like eating enough protein and focusing on muscle tissue with its male marketing focus on protein supplements and lack of understanding in the difference in the sexes.
You can add muscle to your body and focus on fueling for it without concern that you will become a bodybuilder. Professional female body builders work very hard to build up their muscle tissue to the level you see in competitions, and gaining muscle at that level is challenging due to the differences in amount of testosterone in men and women. If getting huge biceps is not an aesthetic goal for you, have no fear that you’re going to suddenly achieve it. But it is attainable for you if you choose to pursue it – I recommend a personal trainer who specializes in body building if this is of interest, and a willingness to spend years in pursuit of that goal.
V. Building muscle at different stages of your menstrual cycle
How do we build muscle? In a previous article, I described the process by which we gain muscle. In a nutshell, muscles working against a progressively challenging load leads to increases in muscle mass – a process referred to as hypertrophy. Hypertrophy is a thickening of the muscle fibers, creating stronger muscles.
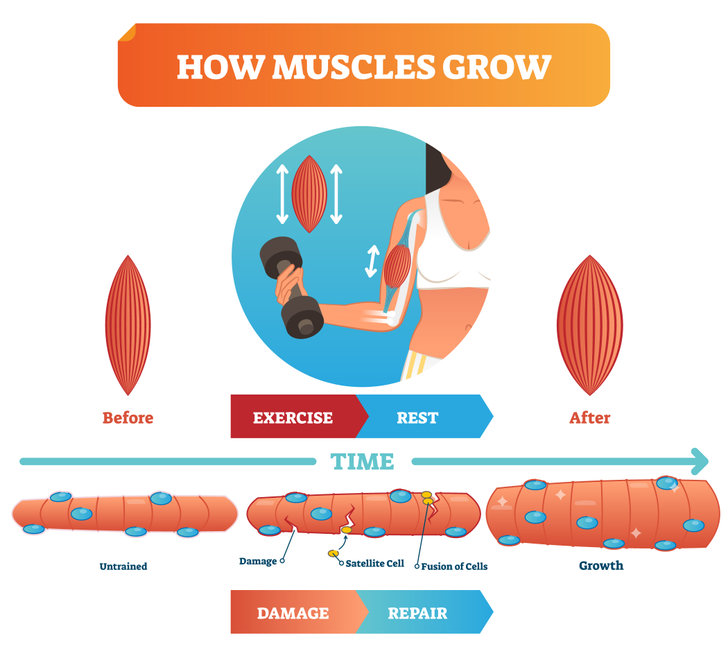
These adaptation to an increased load happens when we also fuel and rest properly. As the body gets used to the challenges you present it with, you need to vary the type of load in order to continue to drive adaptations. And for women, there are considerations due to the presence (or absence) of estrogen.
When you’re still having a regular cycle, remember that in the first half of your cycle (from when you get your period until you ovulate) estrogen is higher. This estrogen is estradiol, or E2 and it’s the most anabolic (muscle building) of the estrogen hormone trio (E1, E2, E3). During this phase, you also have a greater ability to use carbohydrates than you do post ovulation (be mindful of your consumption of sugary foods after you ovulate, and prioritize protein)(12 )(13)(14 ).
So if you’re still cycling regularly, take advantage of this first stage of your cycle (follicular phase) by pushing harder in your workouts (14) to create those muscular adaptations that lead to lean mass development.
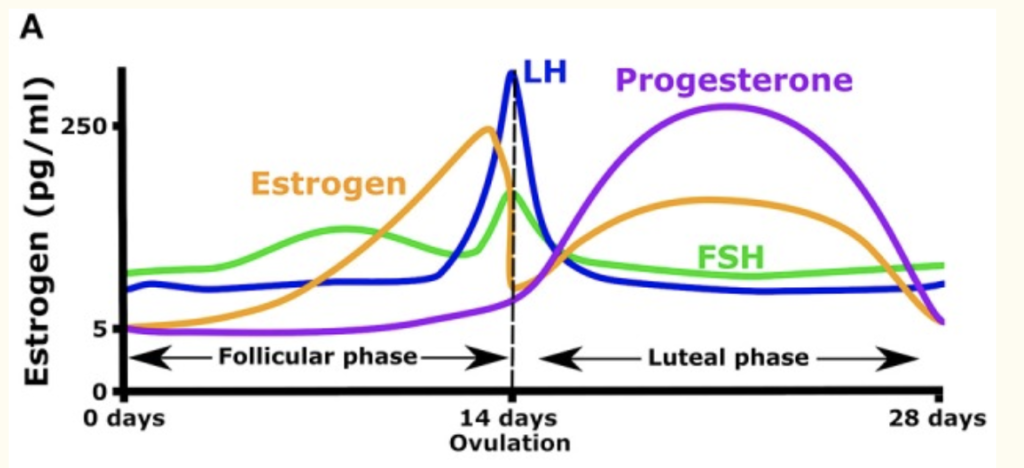
Balanced training is essential in the follicular phase as overtraining will contribute to more inflammation, elevated cortisol, and muscle protein breakdown. Not fueling and managing stress appropriately around your tough workouts will also have this effect and undermine your ability to build muscle.
After you ovulate (luteal phase), progesterone is going to be elevated, which will create a higher state of inflammation in your body as it prepares the uterine lining. Your basal body temperature is elevated, which may mean you get less deep sleep. Don’t push yourself as hard in this phase of your cycle – notice your energy needs and feel free to take the intensity down a notch or two.
You can really back off on the intensity of your training in the days or week leading up to your period, as you may notice less energy due to hormone levels shifting. I tend to do lower impact workouts during the days before my period as I just feel more tired. I’ll swap in yoga, mobility or just slower, less intense resistance training. Or simply take an extra rest day or 3 as needed.
How I adjust a program to match up with my cycle is if I’m following a 4-week training program for instance, I simply extend it a bit longer so I can add some days of lower intensity work in the week where I have less drive. I do some low impact workouts, yoga,..


